
(Photo by Iker Urteaga on Unsplash)
工作项目需要,最近在研究Airflow,Apache基金会下的一款任务流管理工具,基于Python而生,官网链接在此。这几天弄清楚了PythonOperator中不同Task之间如何传递参数,目前主要找到了两种方法。
第一种方法是使用Variable.set和Variable.get方法;第二种方法使用Xcoms。
方法1:
在Airflow自带的example_python_operator这个DAG里面,从airflow.models导入Variable模块,使用Variable.set先设置变量;然后在另外一个Task里面使用Variable.get获取参数。设置变量时可以使用deserialize_json参数,deserialize_json=True时,表示被设置的变量为序列化对象;后面使用Variable.get获取该变量的地方,也需要对应加上deserialize_json参数。
Variable.set和Variable.get方法直接查看Source code for airflow.models.variable这份文档。
在example_python_operator这个DAG里面,如下方式即可实现不同Task之间传递参数。
|
|
执行结果请看下面红色方框处:
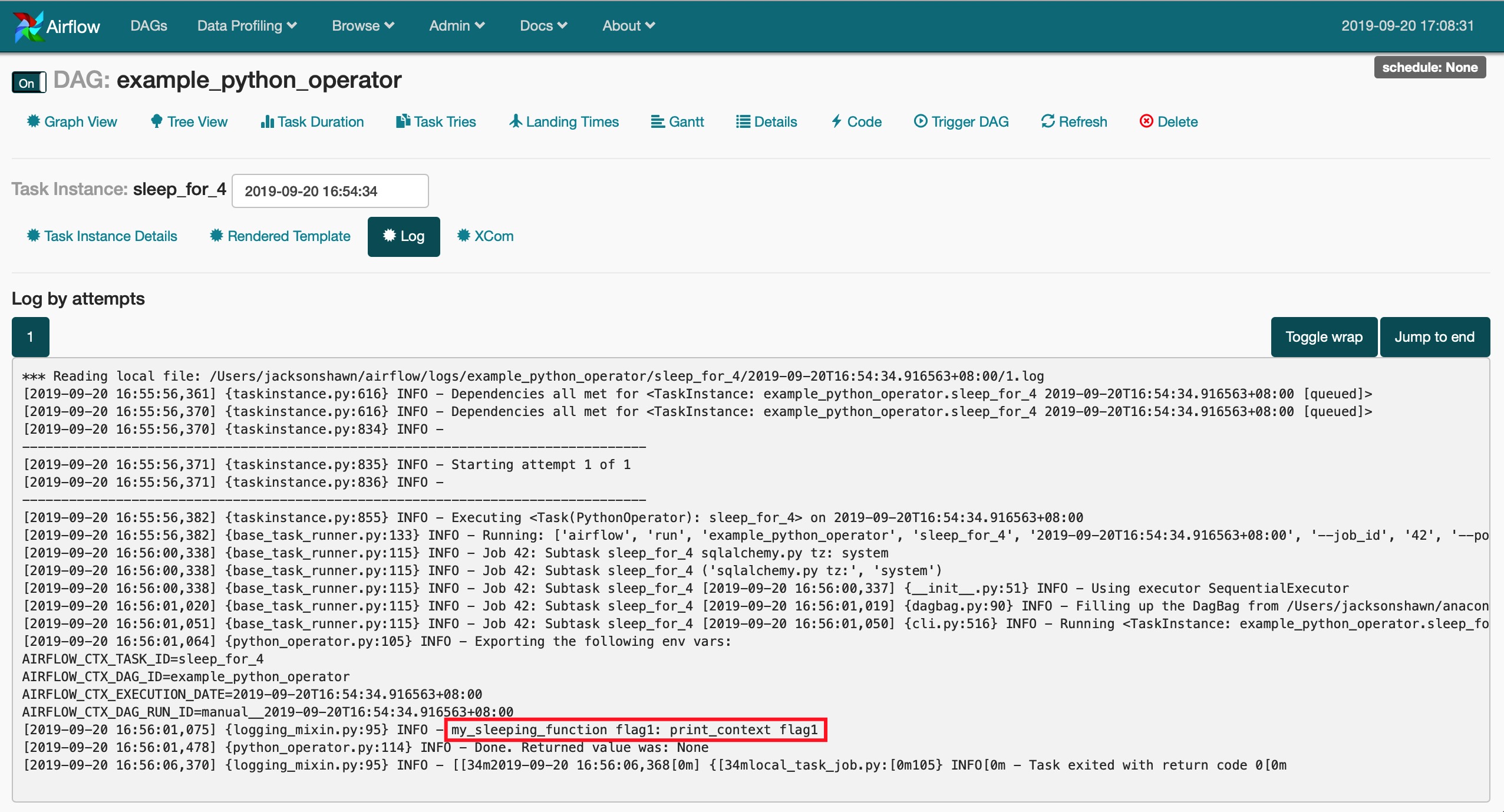
方法2:
在Task A中使用return返回要被Task B引用的变量;在Task B中直接使用xcom_pull即可引用该变量。参考代码如下。
|
|
执行结果:
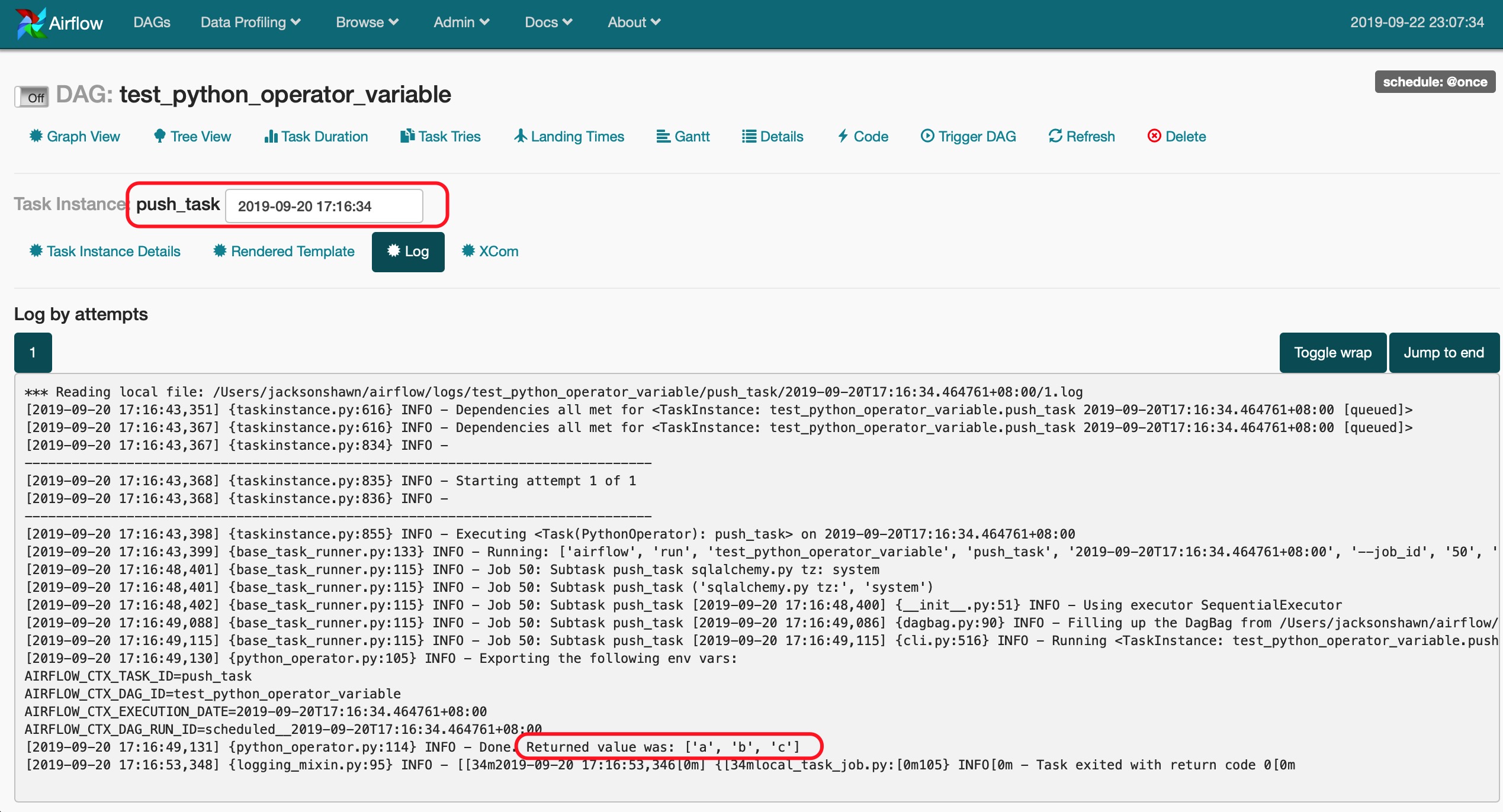
push_task这个Task执行完后Return的值如下所示。
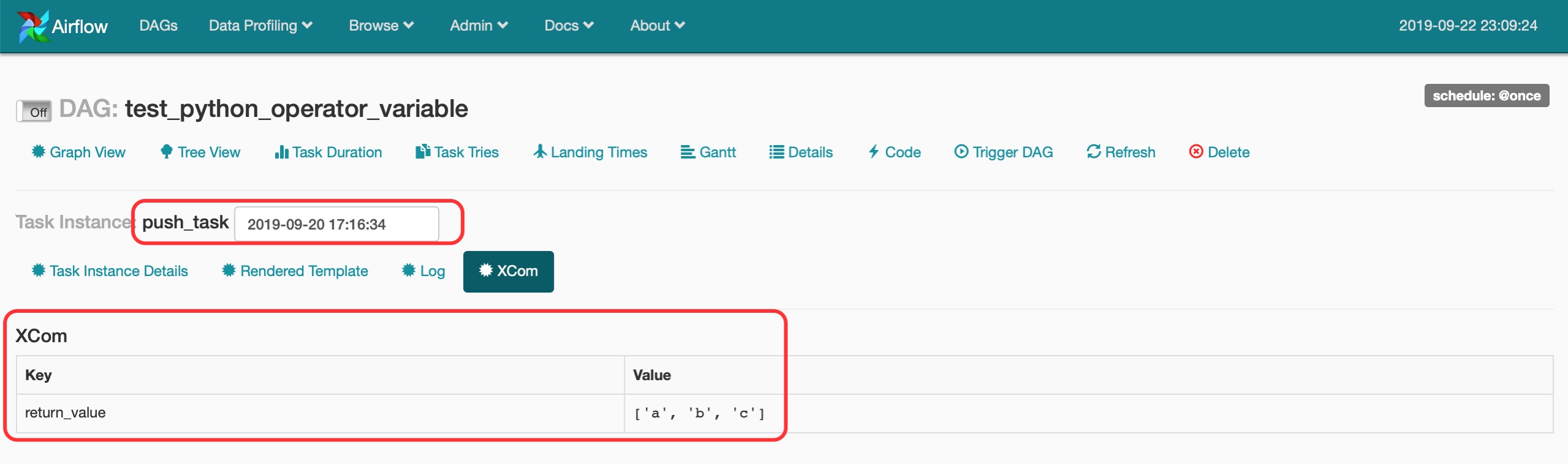
push_task这个Task执行完后Xcom的内容如下所示。
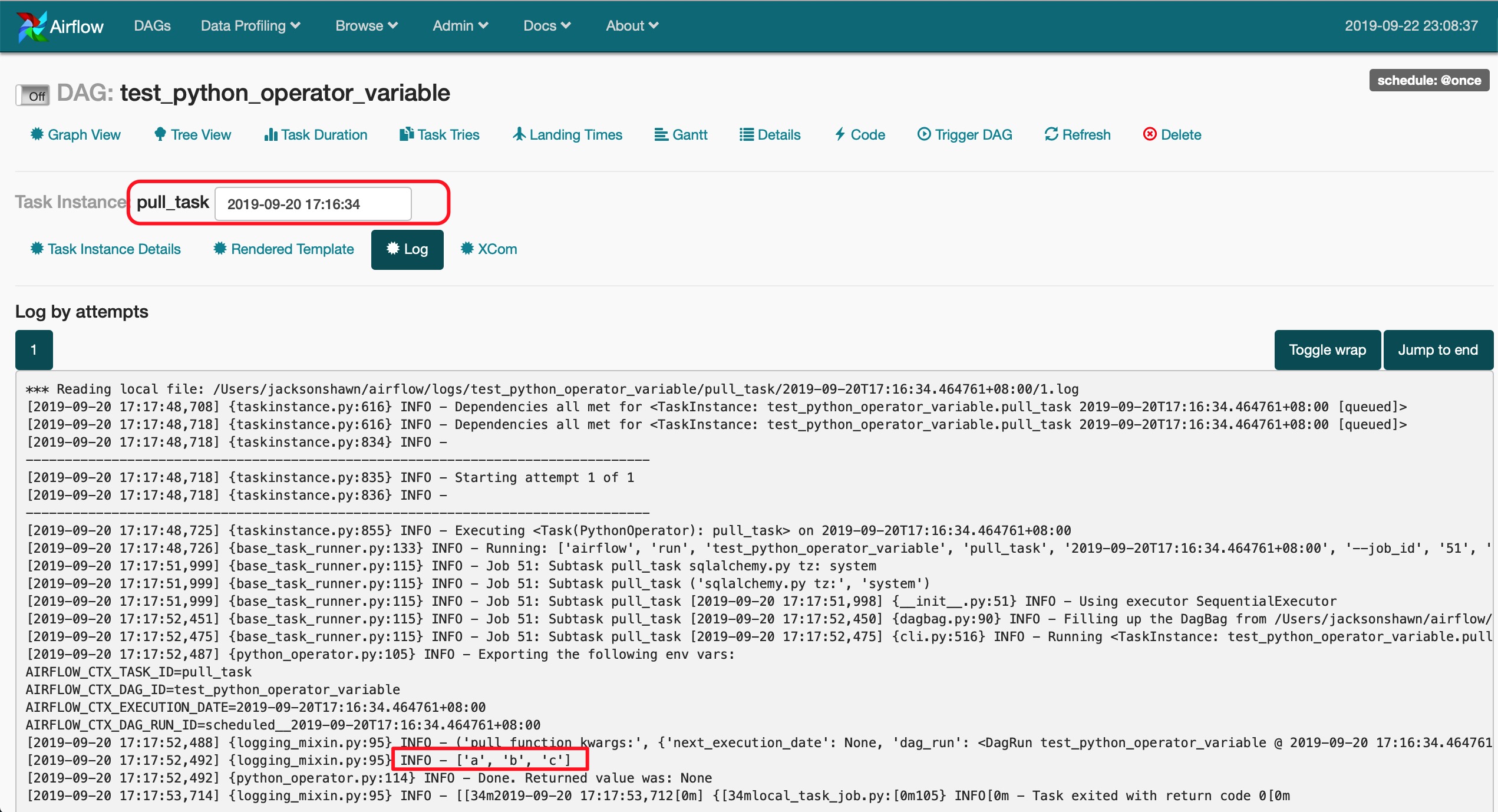
pull_task执行过程中打印出了变量ls的值,说明参数传递成功。
方法2是从StackOverflow翻出来的,参考链接见这里。
ti是kwargs字典里面内置的变量,表示的是当前这个Task Instance。
